Reply To All activity
An activity that creates a message and addresses it to the sender and all recipients of the original message in Microsoft Outlook.
Configure the Reply To All activity
To configure the Reply To All activity, do the procedure in this topic.
Good to Know
- To send an email notification, click
Advanced
 >
Email Notifications
>
Email Notifications  .
. For more information, refer to Email Notifications screen (Process Activities).
- In most text fields, you can use process data variables as an alternative to literal data values.
- You can configure whether this activity waits for other activities before it runs.
For more information, refer to How Do I Configure an Activity to Wait for Other Incoming Activities?
- This section shows the configuration settings on the configuration screens for this activity. Other configuration settings apply to system activities. For more information, refer to:
- Some information about third-party integrations is outside the scope of the AgilePoint NX Product Documentation. It is the responsibility of the vendors who create and maintain these technologies to provide this information. This includes specific business use cases and examples; explanations for third-party concepts; details about the data models and input and output data formats for third-party technologies; and various types of IDs, URL patterns, connection string formats, or other technical information that is specific to the third-party technologies. For more information, refer to Where Can I Find Information and Examples for Third-Party Integrations?
How to Start
- Open Process Builder.
For information about how to open this screen, refer to Process Builder.
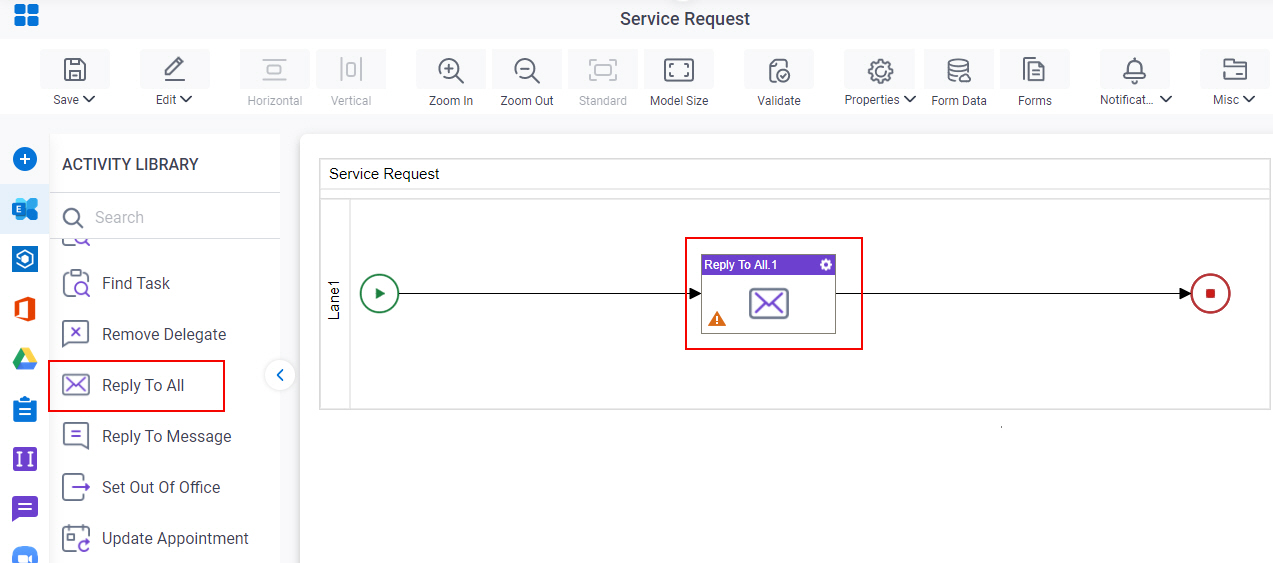
- In Process Builder, in the Activity Library,
open the Exchange Server tab.
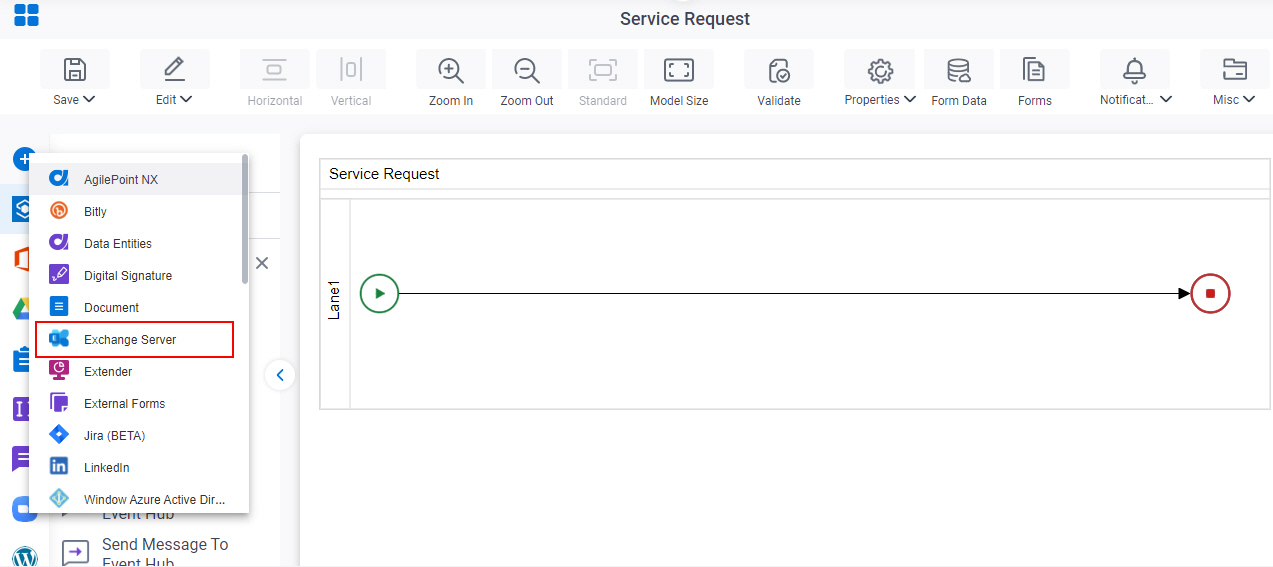
- On the Exchange Server
tab,
drag the Reply To All
activity onto your process.
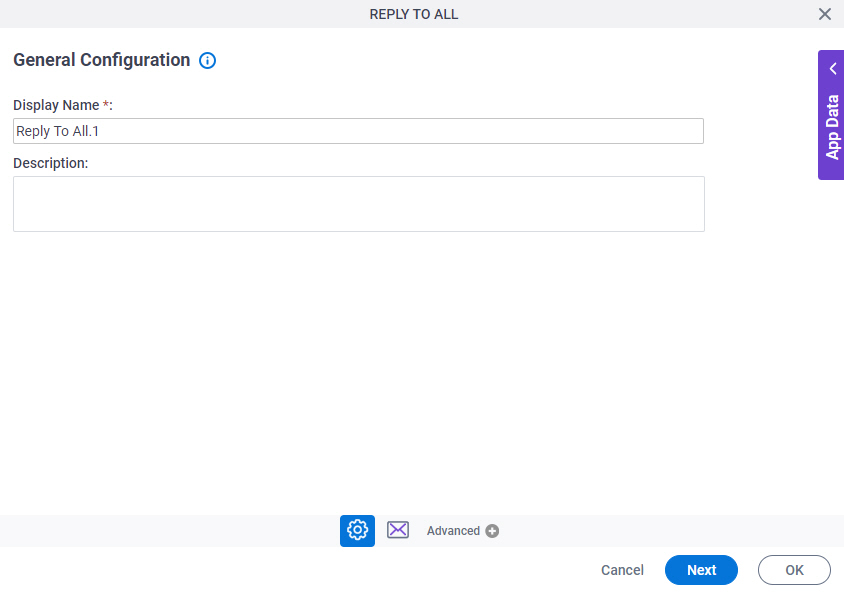
General Configuration
Specifies the basic settings for the Reply To All activity.
Good to Know
- Documentation for this screen is provided for completeness. The fields are mostly self-explanatory.
Fields
| Field Name | Definition |
|---|---|
|
Display Name |
|
|
Description |
|
Reply To All Configuration
Specifies the configuration that creates a message and addresses it to the sender and all recipients of the original message in Microsoft Outlook.
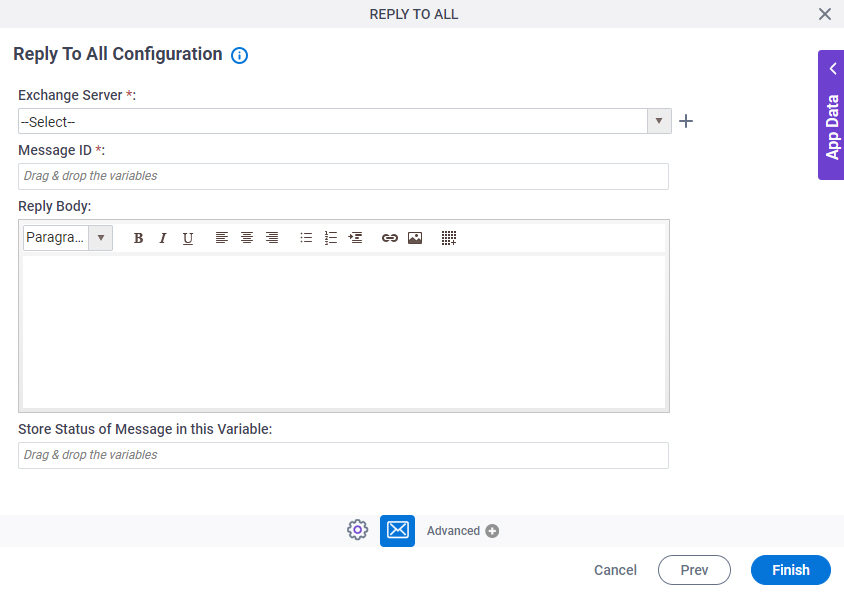
Fields
| Field Name | Definition |
|---|---|
|
Exchange Server |
|
|
Create |
|
|
Message ID |
|
|
Reply Body |
|
|
Store Status of Message in this Variable |
|