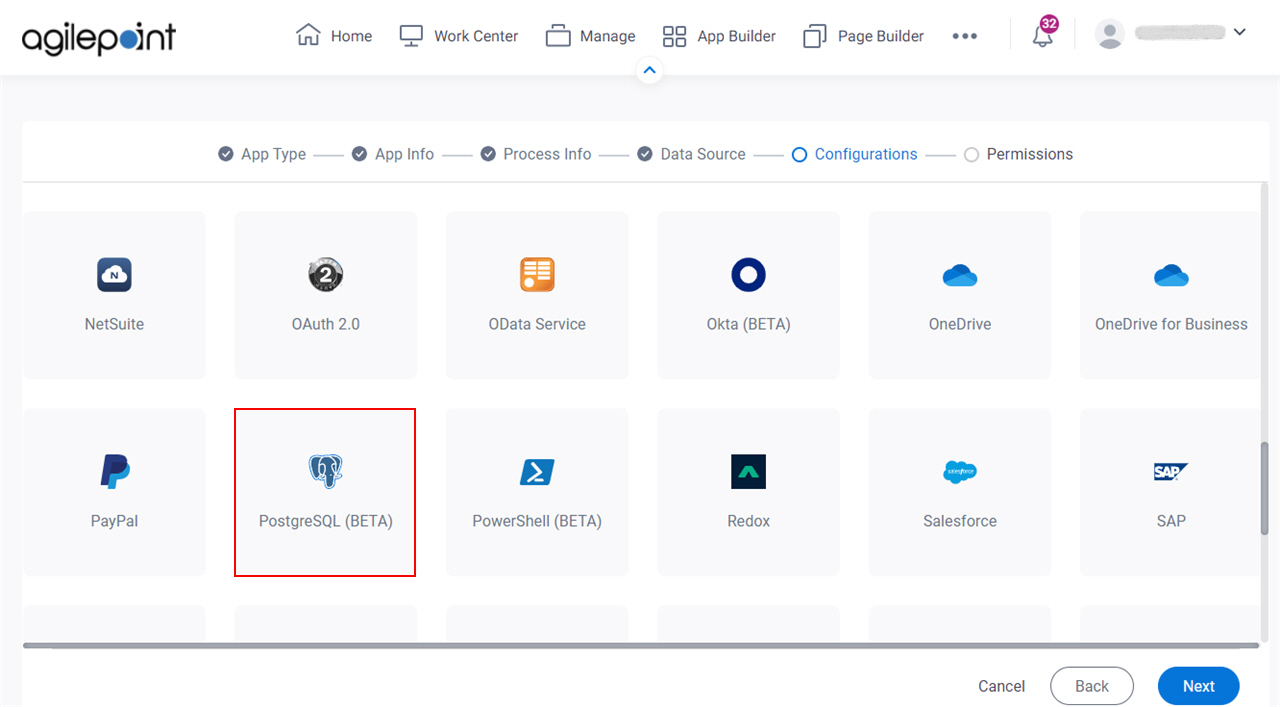
Access Token for PostgreSQL
Configure an access token to connect to PostgreSQL.
Background and Setup
Prerequisites
- AgilePoint NX OnDemand (public cloud), or AgilePoint NX Private Cloud or AgilePoint NX OnPremises v8.0 Software Update 2 or higher.
Good to Know
- In most cases, you can use a global access token or
an app level access token:
- Global access tokens are shared across all users and apps. If you want all process designers and runtime app users in your AgilePoint NX tenant to be able to connect to an external data source, use a global access token. An example is a SharePoint site on an intranet that all employees in a company can access.
- Application level access tokens are shared with all processes in a process-based app, or restricted to use within a form-based app. Use application level access tokens if only process designers or runtime app users for a particular application should access an external system — for example, a Box account that is only used to share files within a small team.
- Access tokens are collections of credentials that are used to authenticate communication directly between AgilePoint NX and an external system. Because it is the AgilePoint NX system that uses these credentials, rather than an app, there is no difference between
design time
and
runtime
access tokens. Access tokens are never checked in or published, and they do not use version control. If you change an access token in the App Builder or Manage Center, the access token changes immediately everywhere the access token is used. Changes to app level access tokens apply to all versions of an app, including running application instances. Changes to global access tokens apply everywhere they are used in AgilePoint NX. You can not roll back an access token to a previous version.
For more information, refer to What Data Is Deleted When I Delete an App or Application Resource?
- This screen may look different in different places. The UI varies for this screen depending upon how you open it. However, the fields for this screen are the same in all places.
- Some information about third-party integrations is outside the scope of the AgilePoint NX Product Documentation. It is the responsibility of the vendors who create and maintain these technologies to provide this information. This includes specific business use cases and examples; explanations for third-party concepts; details about the data models and input and output data formats for third-party technologies; and various types of IDs, URL patterns, connection string formats, or other technical information that is specific to the third-party technologies. For more information, refer to Where Can I Find Information and Examples for Third-Party Integrations?
How to Start
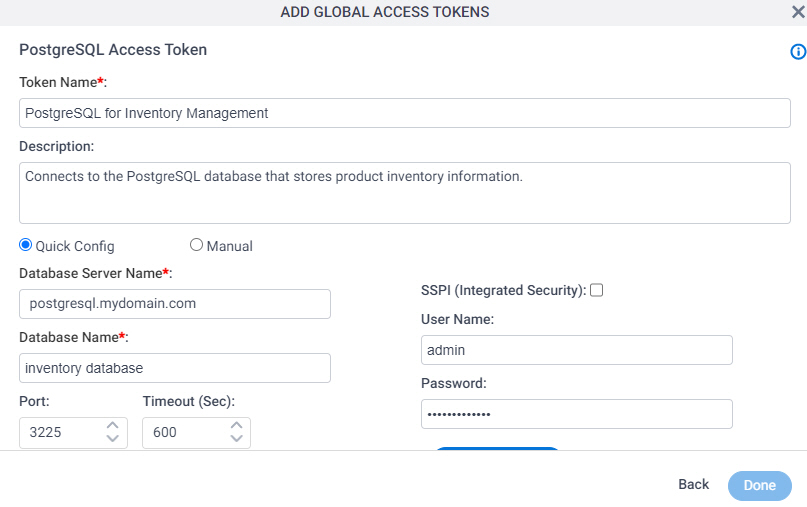
Fields
| Field Name | Definition |
|---|---|
Token Name |
|
Description |
|
Database Server Name |
|
Database Name |
|
Port |
|
Timeout (Seconds) |
|
SSPI (Integrated Security) |
|
User Name |
|
Password |
|
Connection String |
|
Test Connection |
|